Viewing之后
- Model transformation (placing objects)
- View transformation (placing camera)
- Projection transformation
- Orthographic projection (cuboid to “canonical” cube $[-1, 1]^3$)
- Perspective projection (frustum to “canonical” cube)
- Canonical cube to?
继续:将之前得到的立方体绘制到屏幕上。
Canonical Cube to Screen
概念定义
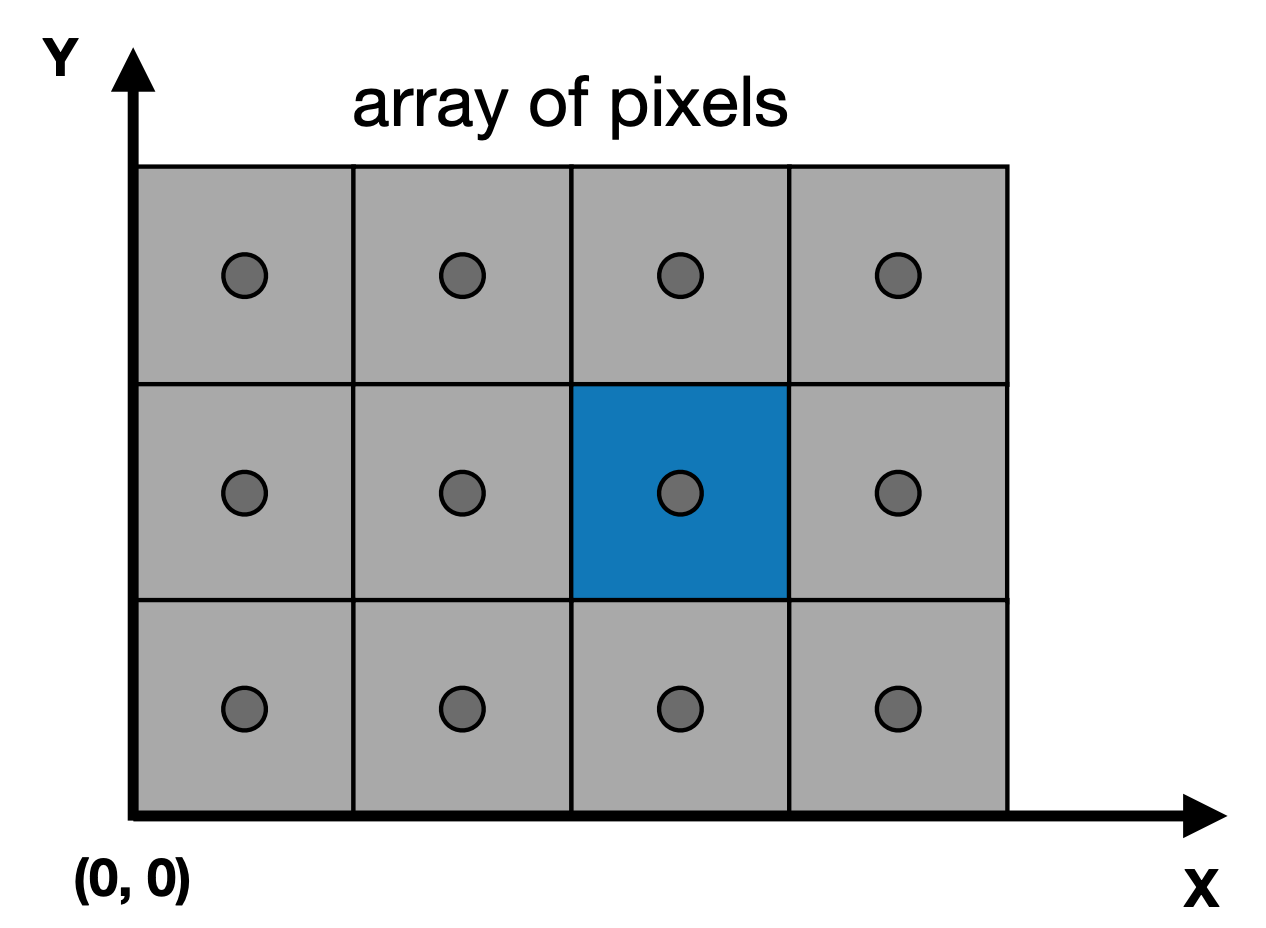
- What is a screen
- An array of pixels
- Size of the array: resolution 表示像素的多少。
- A typical kind of raster display
- Raster == screen in German
- Rasterize == drawing onto the screen
- Pixel (FYI, short for “picture element”)
- For now: A pixel is a little square with uniform color 简化表示
- Color is a mixture of (red, green, blue)
Screen space
规则:
- Pixels’ indices are in the form of $(x, y)$, where both x and y are integers.
- Pixels’ indices are from $(0, 0)$ to (width - 1, height - 1).
- Pixel $(x, y)$ is centered at $(x + 0.5, y + 0.5)$ . 坐标实际中心
- The screen covers range $(0, 0)$ to (width, height).
操作方法
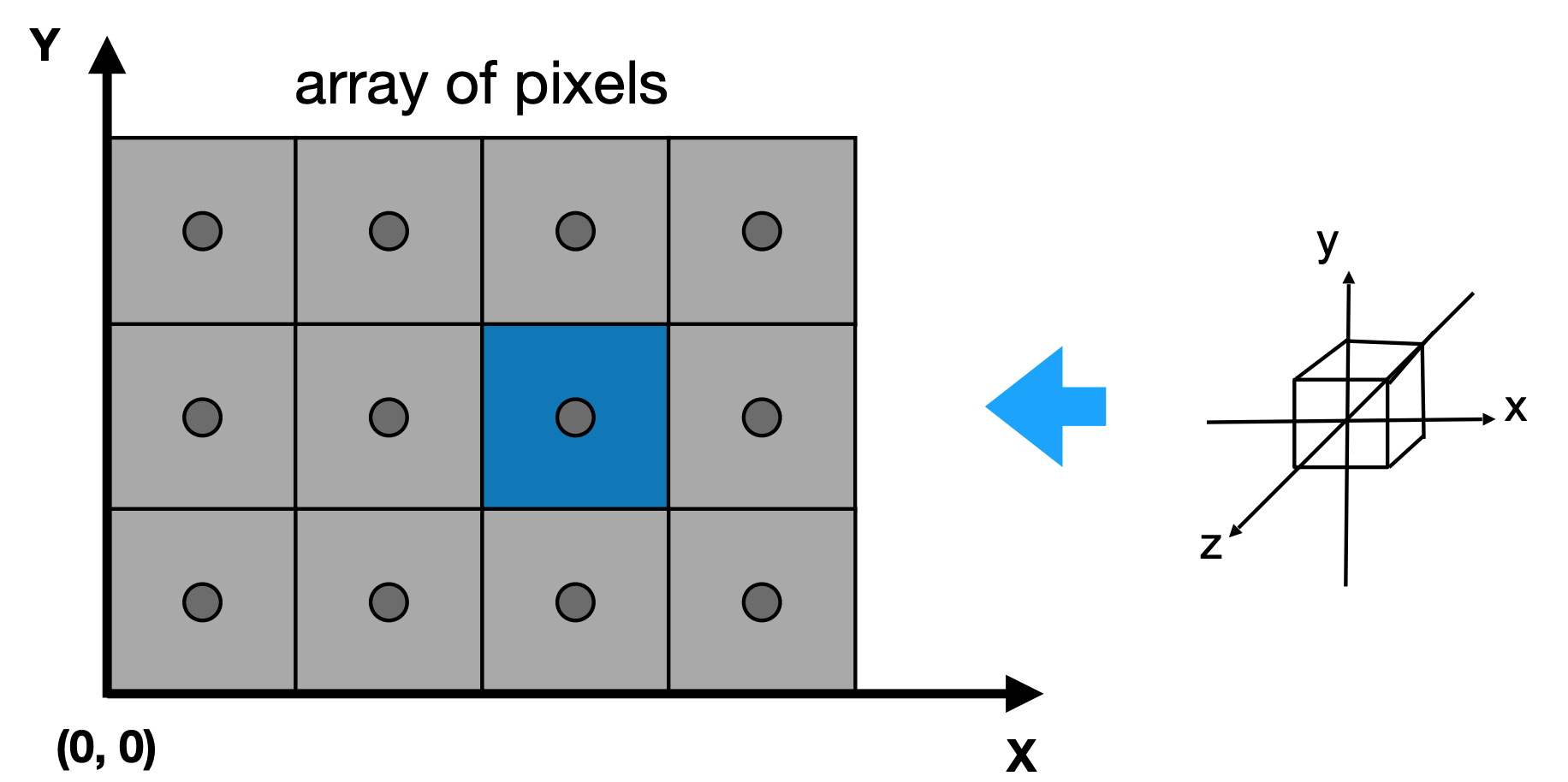
- Irrelevant to z
- Transform in xy plane: $[-1, 1]^2$ to [0, width] x [0, height]
- Viewport transform matrix: 视口变换
$$
M_{\text {viewport}}=\left(\begin{array}{cccc}\frac{w i d t h}{2} & 0 & 0 & \frac{\text { width }}{2} \\
0 & \frac{\text { height }}{2} & 0 & \frac{\text { height }}{2} \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{array}\right)
$$
到此为止得到了2D上的图片。
Rasterizing Triangles into Pixels
接下来,将图片分解为像素,也就是光栅化的过程。
Drawing Machines
- CNC Sharpie Drawing Machine
- Laser Cutters
Different Raster Displays
- Oscilloscope 示波器
- Cathode Ray Tube 阴极射线管
- Television - Raster Display CRT
- Frame Buffer: Memory for a Raster Display
- Flat Panel Displays
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
- LED Array Display
- Electrophoretic (Electronic Ink) Display
Rasterization: Drawing to Raster Displays
Triangles - Fundamental Shape Primitives
Why triangles?
- Most basic polygon
- Break up other polygons
- Unique properties
- Guaranteed to be planar 三角形一定是平面图形
- Well-defined interior 内外容易区分
- Well-defined method for interpolating values at vertices over triangle (barycentric interpolation) 根据顶点的信息可以对其中其中任意一点进行插值。
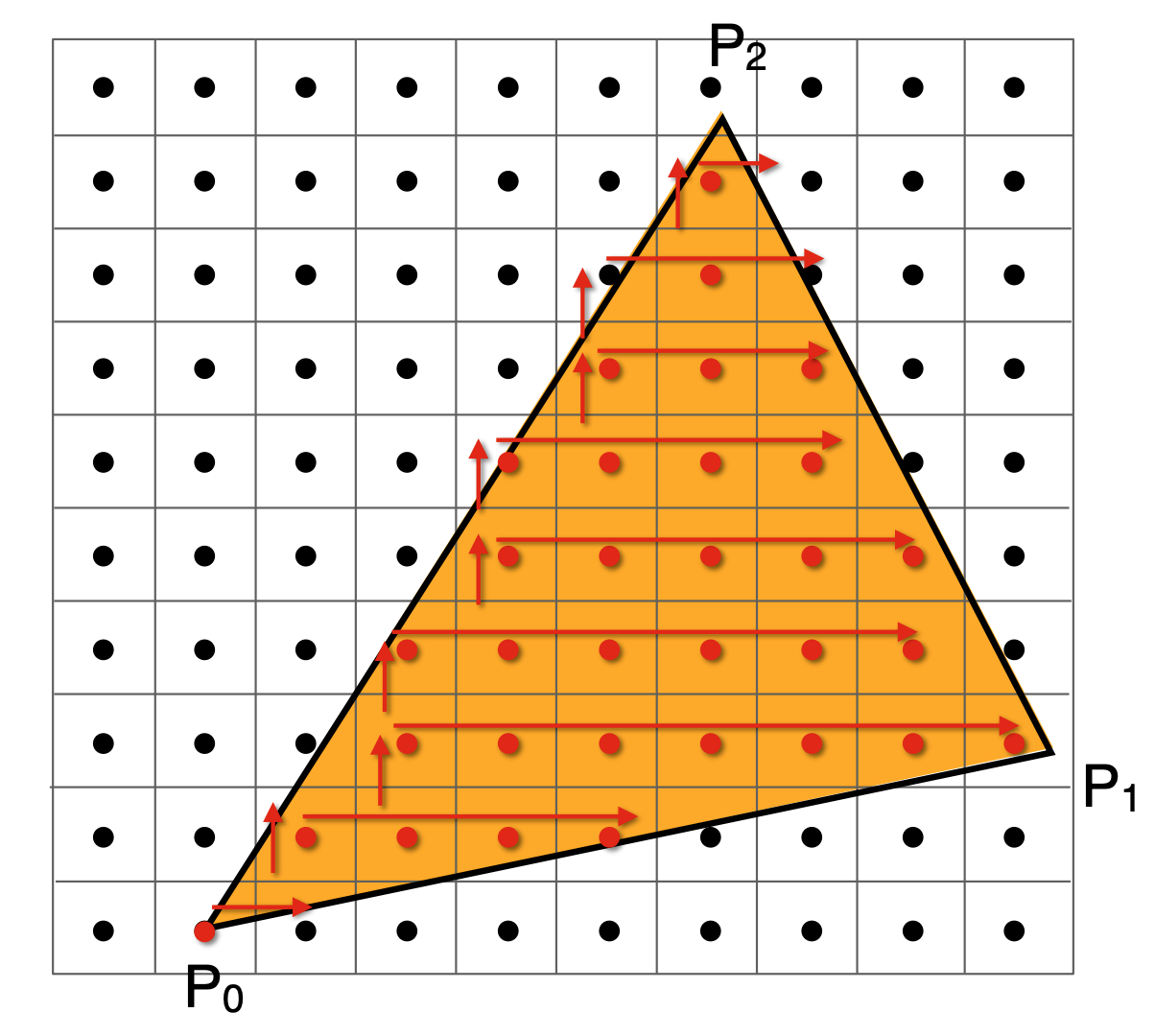
问题:What Pixel Values Approximate a Triangle?
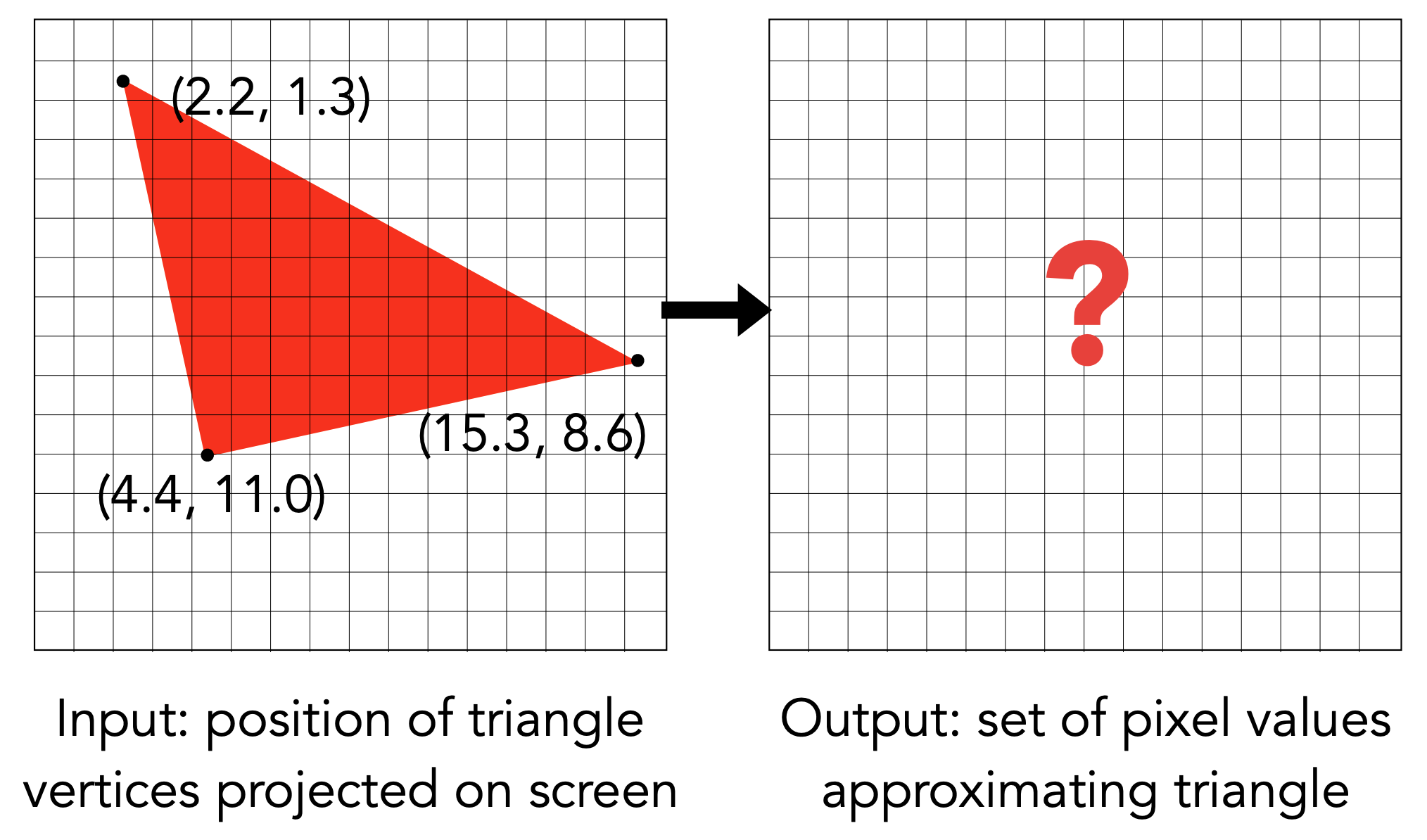
解决方法:Sampling
含义
- Evaluating a function at a point is sampling.
- We can discretize a function by sampling.
for (int x = 0; x < xmax; ++x) output[x] = f(x); - Sampling is a core idea in graphics.
- We sample time (1D), area (2D), direction (2D), volume (3D)
具体过程
- Sample If Each Pixel Center Is Inside Triangle
- Define Binary Function: $\text{inside}(t, x, y)$
- x, y: not necessarily integers
$$
\text{inside}(t, x, y)=
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & \begin{array}{l} \text{Point (x, y) in triangle } t\end{array} \\
0 & \text {otherwise}
\end{array}
\right.
$$
整体过程表示如下:
for (int x = 0; x < xmax; ++x)
for (int y = 0; y < ymax; ++y)
image[x][y] = inside(tri, x + 0.5, y + 0.5);
上述过程中要解决的一个问题是:如何判断点 $(x,y)$ 在三角形内。使用之前cross product中提到的方法。
最后的结果:
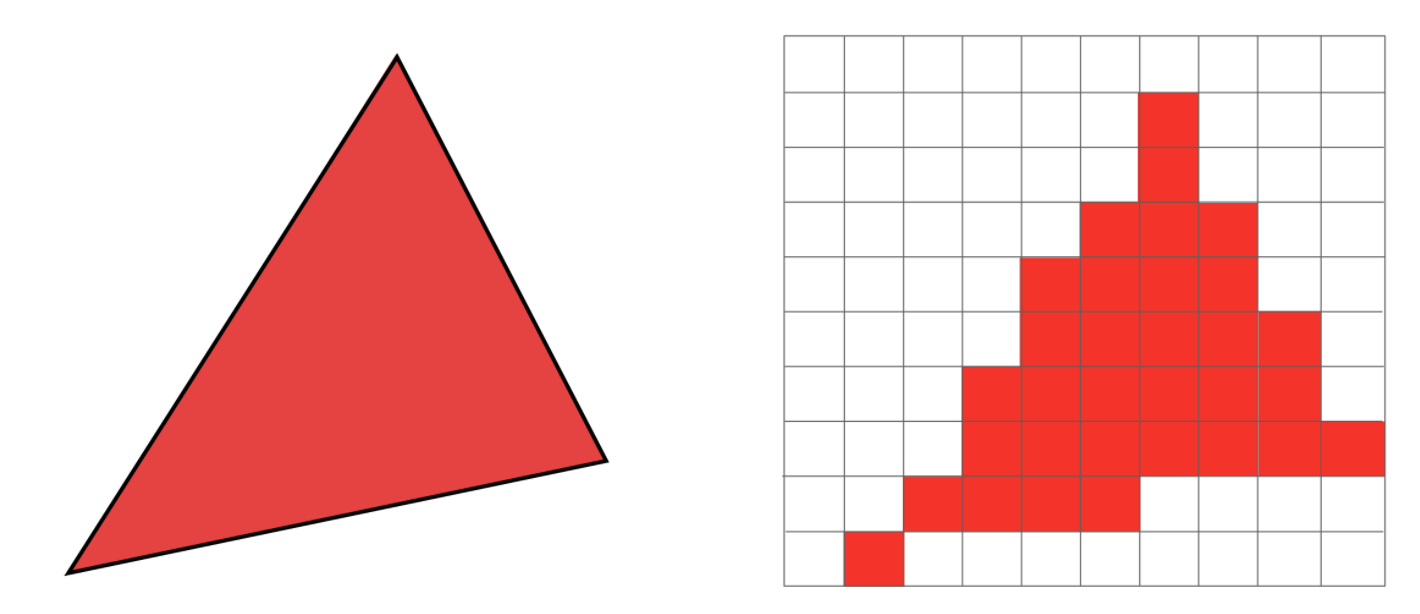
存在锯齿问题!
Edge Cases
Is this sample point covered by triangle 1, triangle 2, or both? 自己决定,不作要求。
优化策略
- 普遍策略:Checking All Pixels on the Screen? Use a Bounding Box!
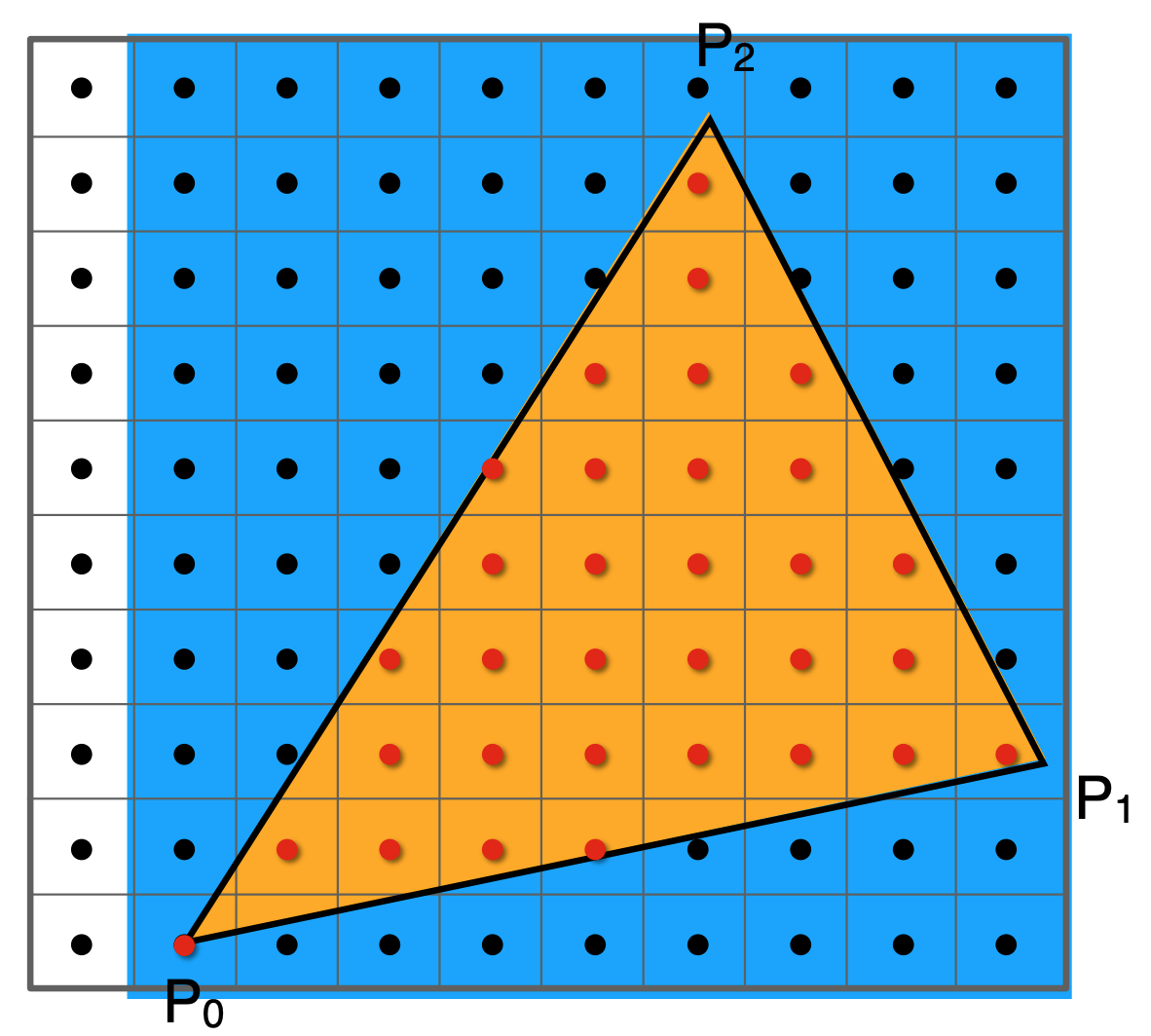
- 进一步优化:Incremental Triangle Traversal,每一行都找边界,suitable for thin and rotated triangles,但是实践起来不太容易。