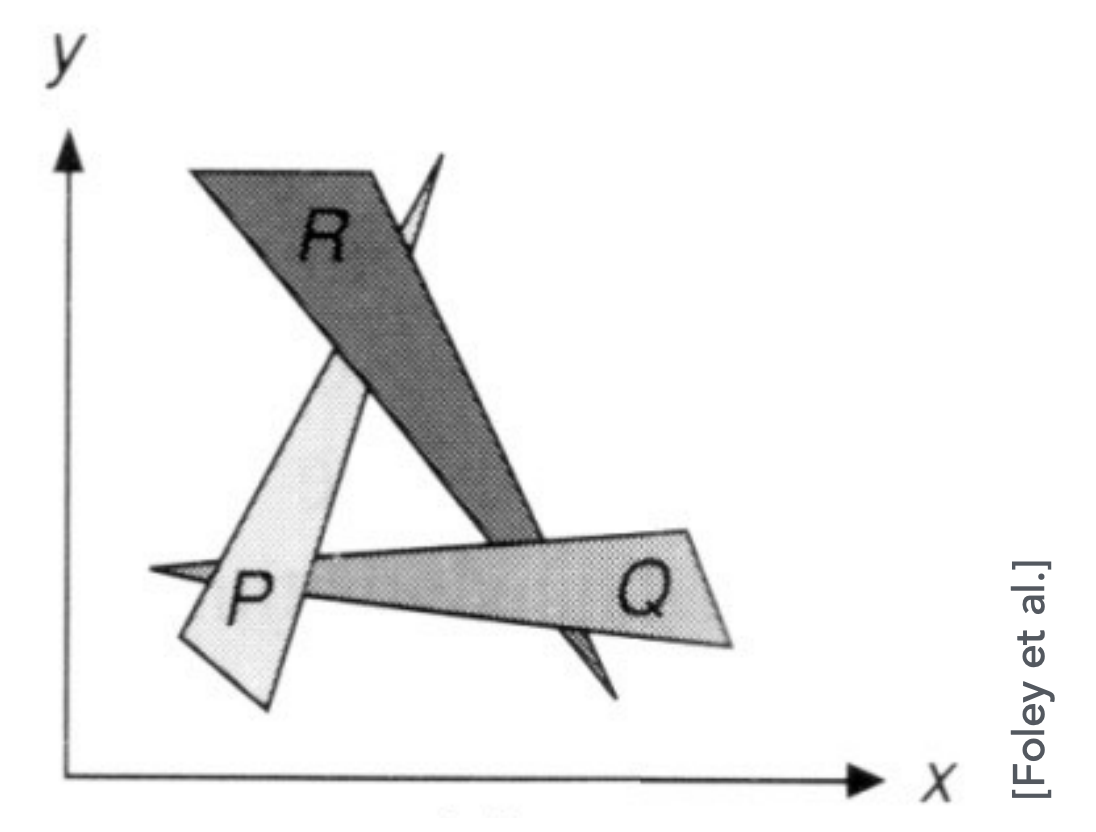
问题:Visibility / occlusion
很多不同的三角形彼此重叠,与相机之间也存在不同的距离,
Painter’s Algorithm
- Inspired by how painters paint
- Paint from back to front, overwrite in the framebuffer
朴素想法
- Requires sorting in depth $(O(n \log n)$ for n triangles)
存在问题
- Can have unresolvable depth order:有时无法得到深度排序;
- 因此实际中不会使用该算法;
Z-Buffer
想法
- Store current min. z-value for each sample (pixel) 所有操作都是针对像素来说的;
- Needs an additional buffer for depth values
- frame buffer stores color values:对应最后的结果;
- depth buffer (z-buffer) stores depth:对应深度缓存的图;
备注:For simplicity we suppose $z$ is always positive (smaller $z$ -> closer, larger $z$ -> further)。
例子
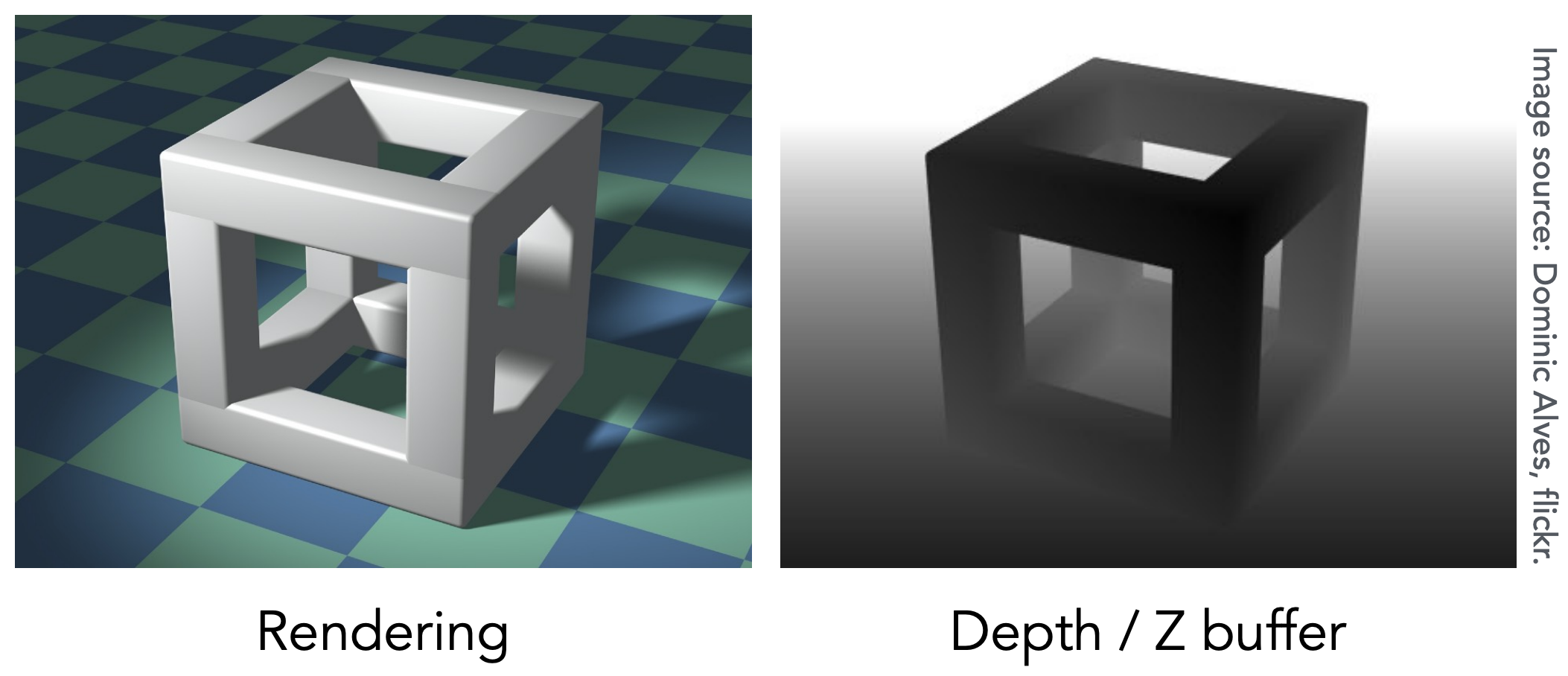
深度值小,对应的是黑色。
Z-Buffer Algorithm
Initialize depth buffer to +inf
During rasterization:
for (each triangle T)
for (each sample (x,y,z) in T)
if (z < zbuffer[x,y]) // closest sample so far
framebuffer[x,y] = rgb; // update color
zbuffer[x,y] = z; // update depth
else
; // do nothing, this sample is occluded
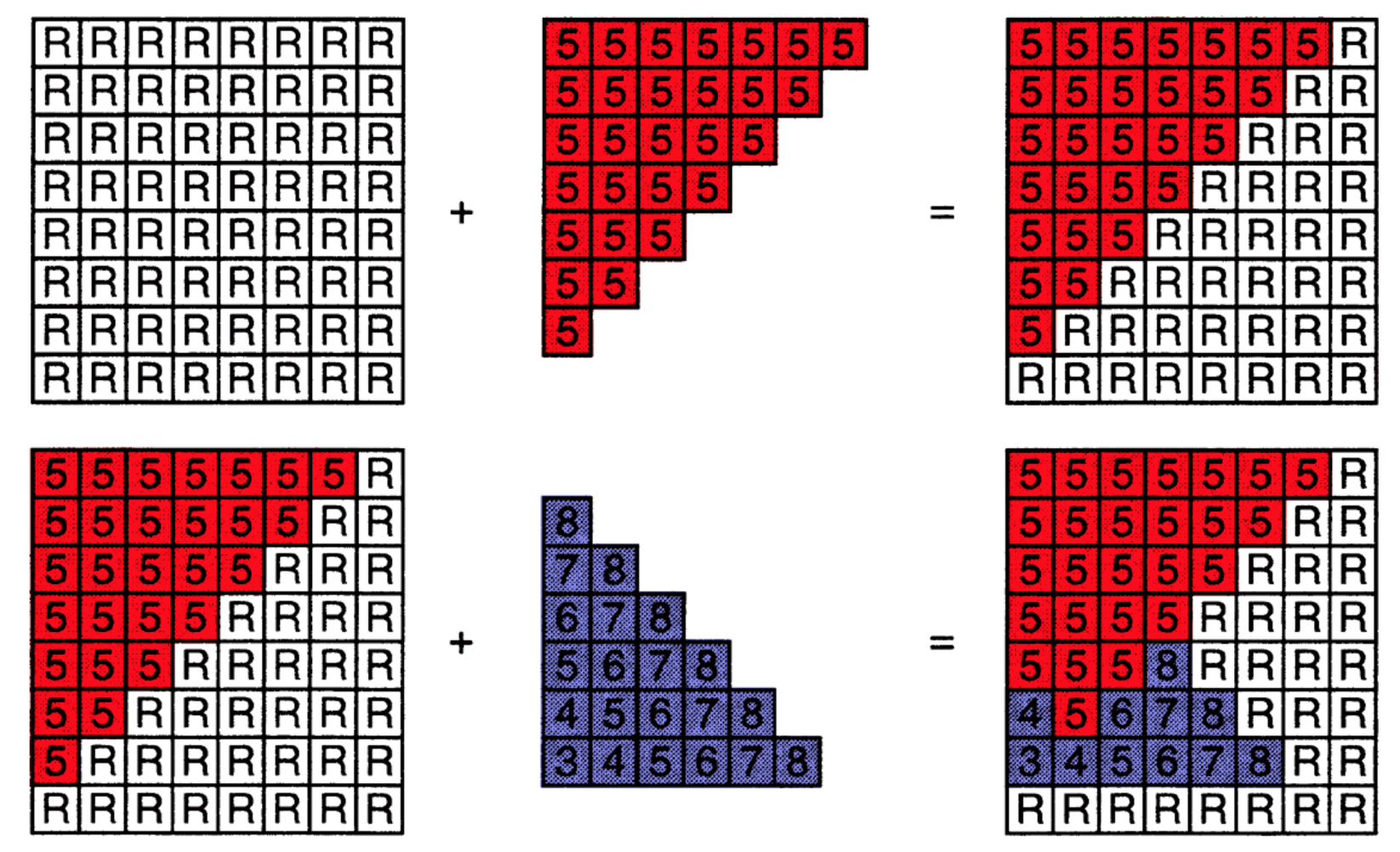
Z-Buffer Complexity
Complexity
- $O(n)$ for n triangles (assuming constant coverage)
How is it possible to sort n triangles in linear time?
- 这里并没有对深度信息进行排序;
Drawing triangles in different orders?
- 结果仍然相同,绘制三角形的顺序不影响最终的结果(不同三角形之间的深度值不存在重复)。
总结
- Most important visibility algorithm
- Implemented in hardware for all GPUs

