Ways to Represent Geometry
Implicit Representations
含义
这种方法不会具体描述集几何物体上的每个点,而是描述所有的点满足的数学关系。
Based on classifying points: Points satisfy some specified relationship.
$$
f(x, y, z) = 0
$$
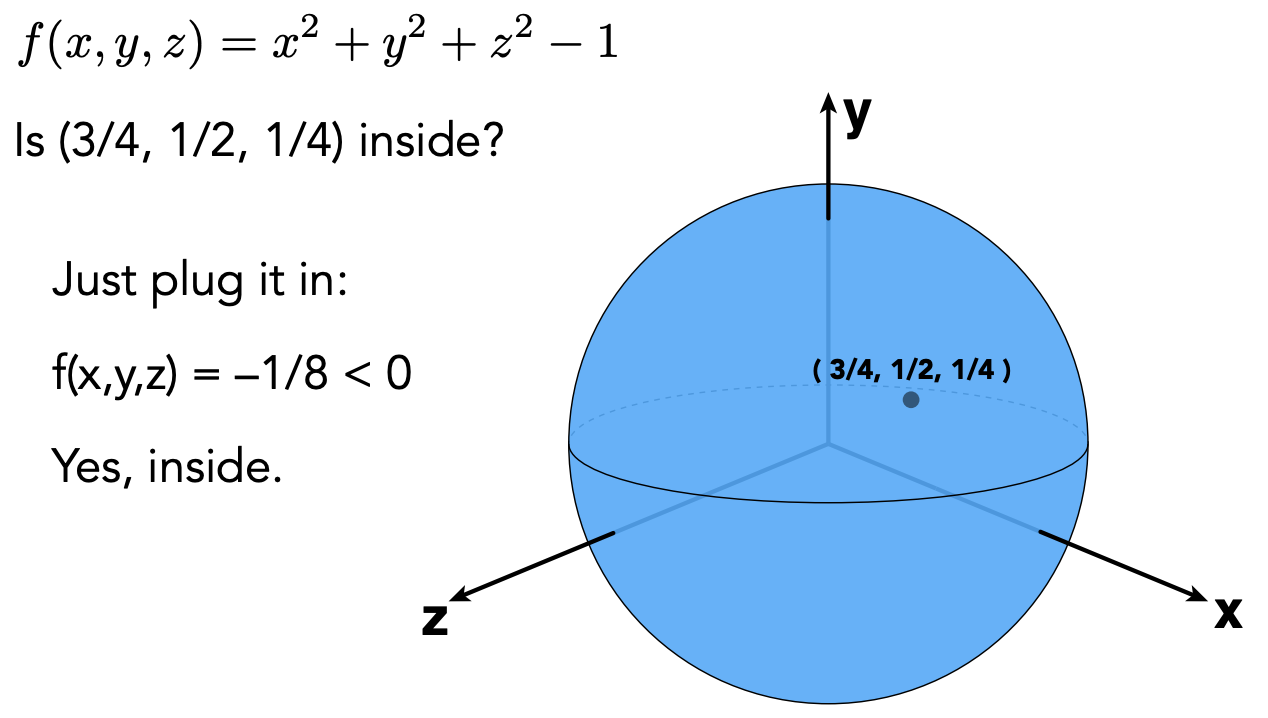
例如球体:
$$
f(x) = x^2 + y^2 + z^2 - 1
$$
优点
- Inside/Outside Tests Easy
缺点
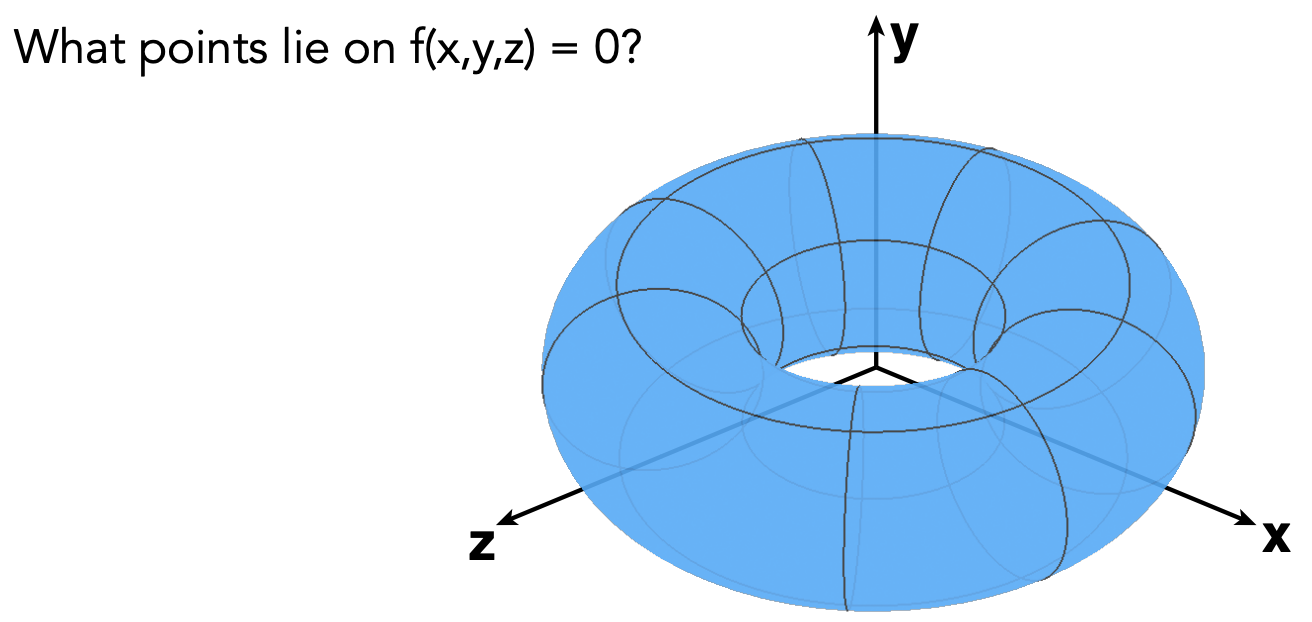
- Sampling Can Be Hard:可能很难看到该表示对应的具体几何形状是什么; $$
f(x, y, z)=\left(2-\sqrt{x^{2}+y^{2}}\right)^{2}+z^{2}-1
$$
Explicit Representations
All points are given directly or via parameter mapping
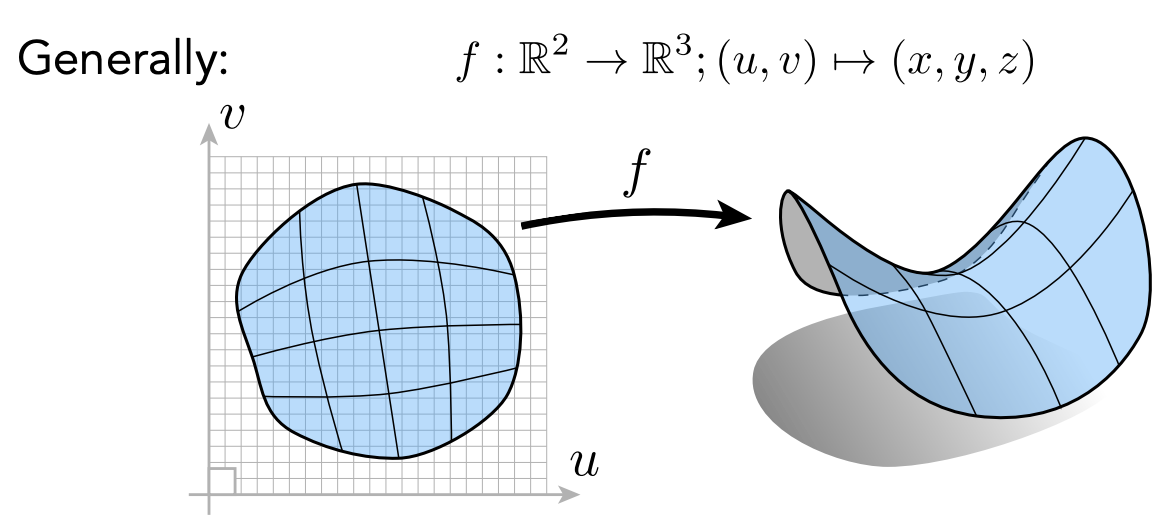
优点
- Sampling Is Easy
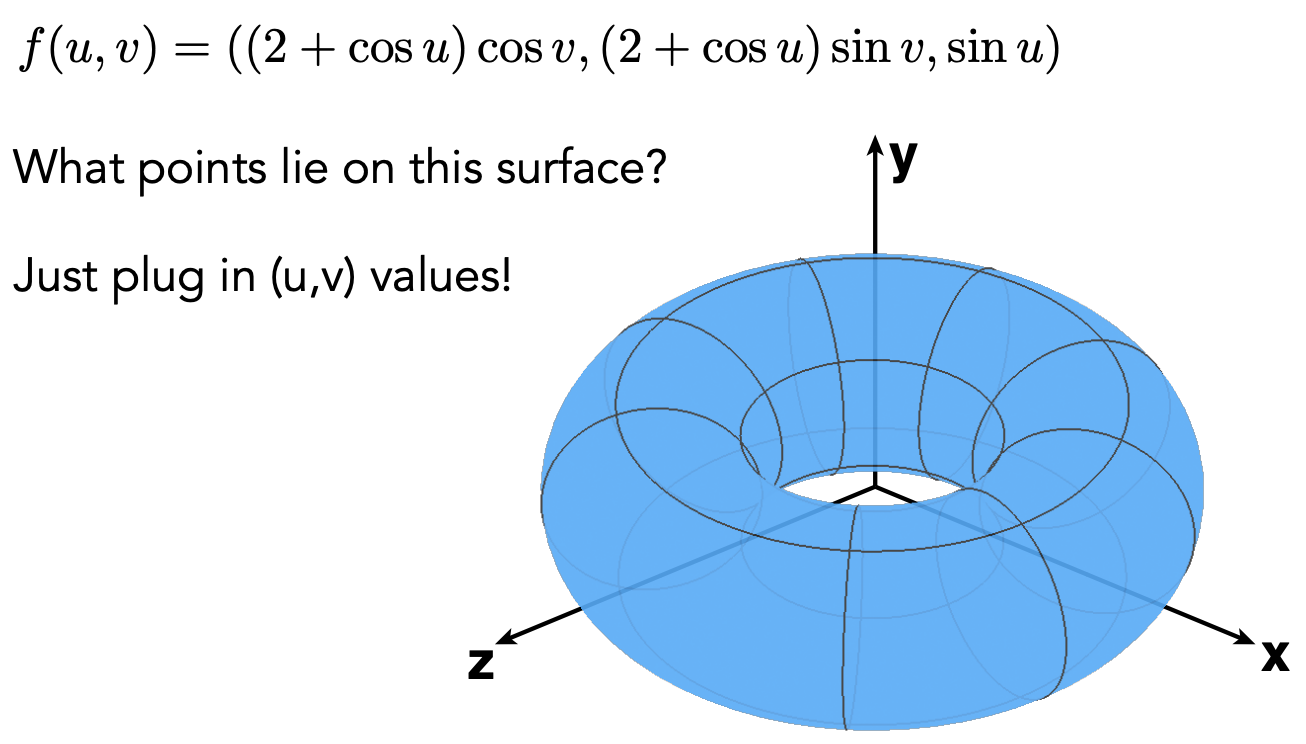
缺点
- Inside/Outside Test Hard
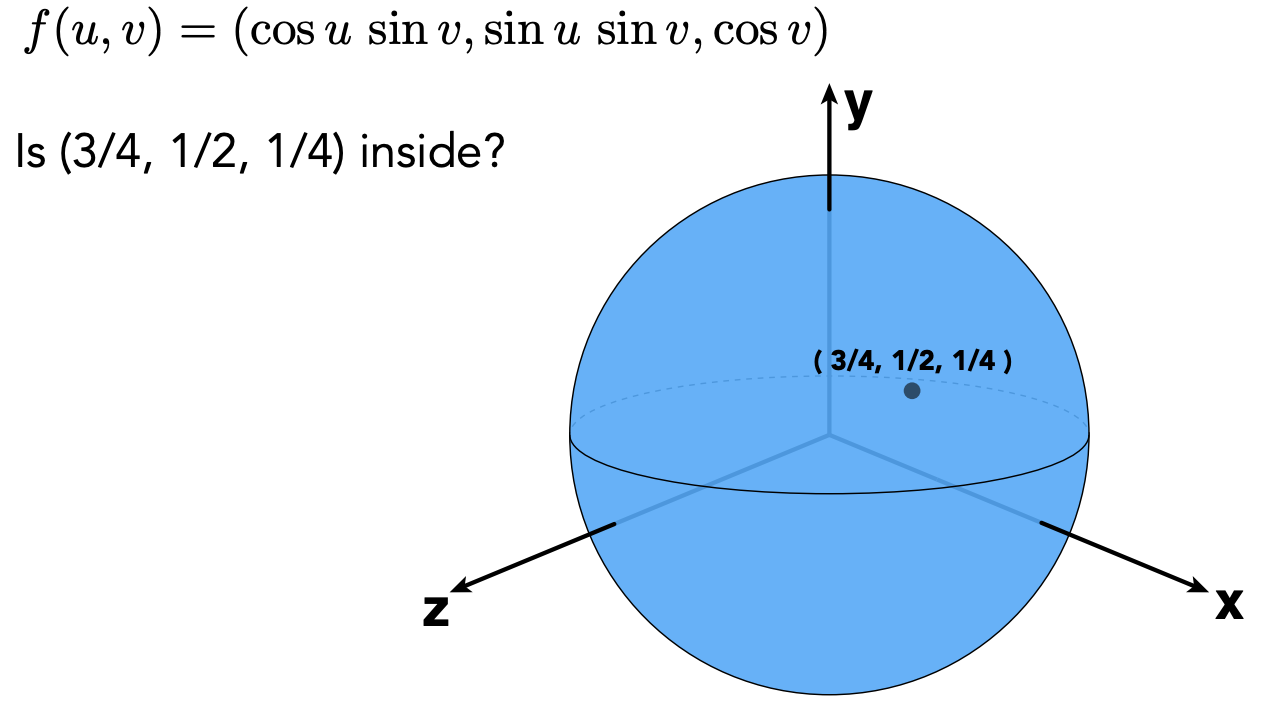
总结
- No “Best” Representation
- Best Representation Depends on the Task!
不同类型的Implicit Representations
Algebraic Surfaces
Surface is zero set of a polynomial in $x, y, z$ .
使用数学公式表示:
- 不直观,无法判断具体形状;

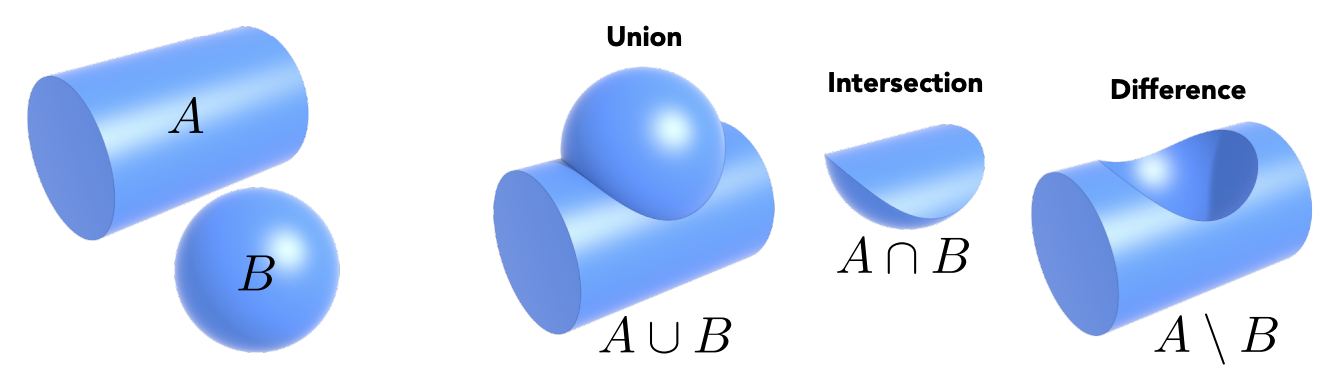
Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG)
Combine implicit geometry via Boolean operations.
Distance Functions
Instead of Booleans, gradually blend surfaces together using Distance functions.
Distance function giving minimum distance (could be signed distance) from anywhere to object.
对任何几何物体,不直接描述其表面,而是描述空间上任意一点到这个集合物体表面的最小距离。
这个最小距离是有符号的:
- 当空间上的点在物体内部,则到该物体表明的距离为负值;
- 当空间上的点在物体外部,则到该物体表明的距离为正值;
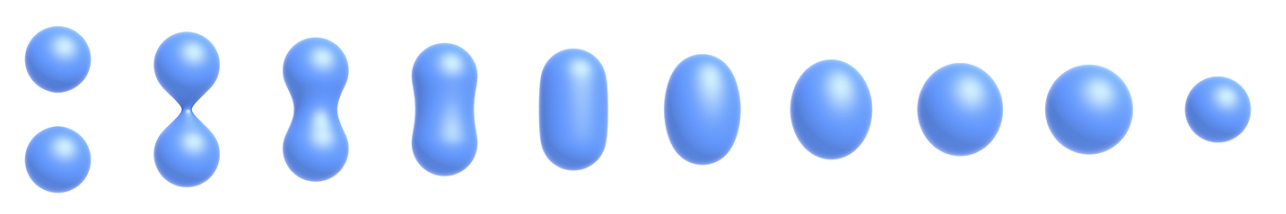
对于每个几何物体都可以计算出其对应的距离函数,这种函数一般将任意一点当做参数,同时定义对应的几何物体表面(这个表面只是一种泛化的说法,其可以是球体的球心,圆的圆心),例如定义球的距离函数如下:
float sdf_sphere (float3 p, float3 c, float r)
{
return distance(p,c) - r;
}
参考资料:
例子:Blending a moving boundary
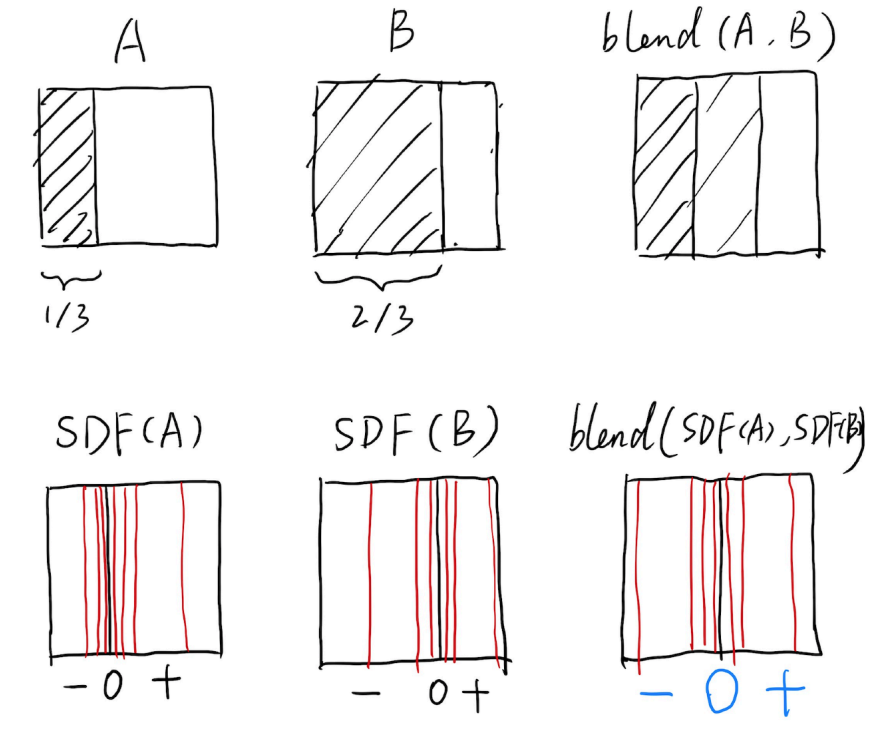
上图中,将A中阴影部分的右边界定义为物体表面,则得到其对应的距离函数在其下方所示。通过对A和B两个物体的距离函数进行融合,可以得到融合后的物体的拓扑结构。
对于任意两个几何物体的blending的操作示意图如下:
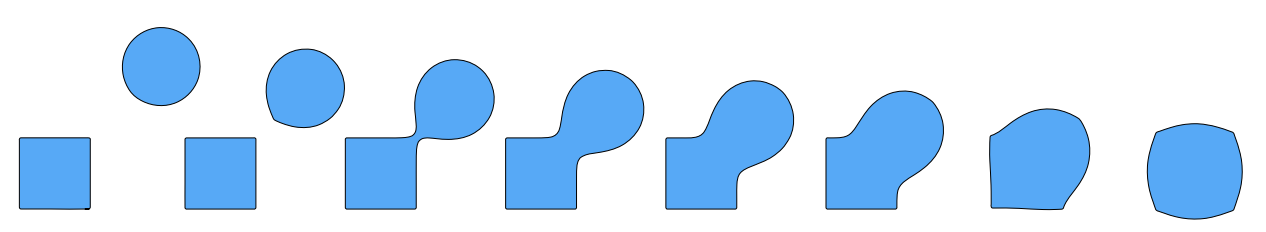
Level Set Methods
问题
Closed-form equations are hard to describe complex shapes.
这种方法针对的问题是:不是任何几何图形都有对应的数学解析形式,面对这种情况,可以通过grid的方式将距离函数表示出来。
解决方法
store a grid of values approximating function.
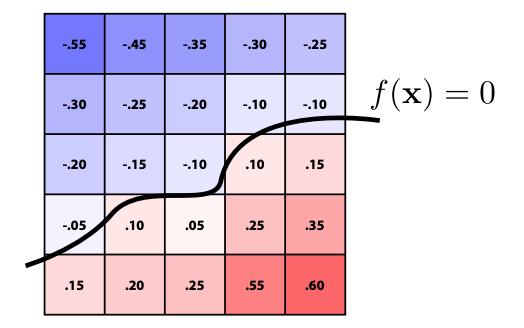
Surface is found where interpolated values equal zero.
优点
Provides much more explicit control over shape (like a texture).
应用
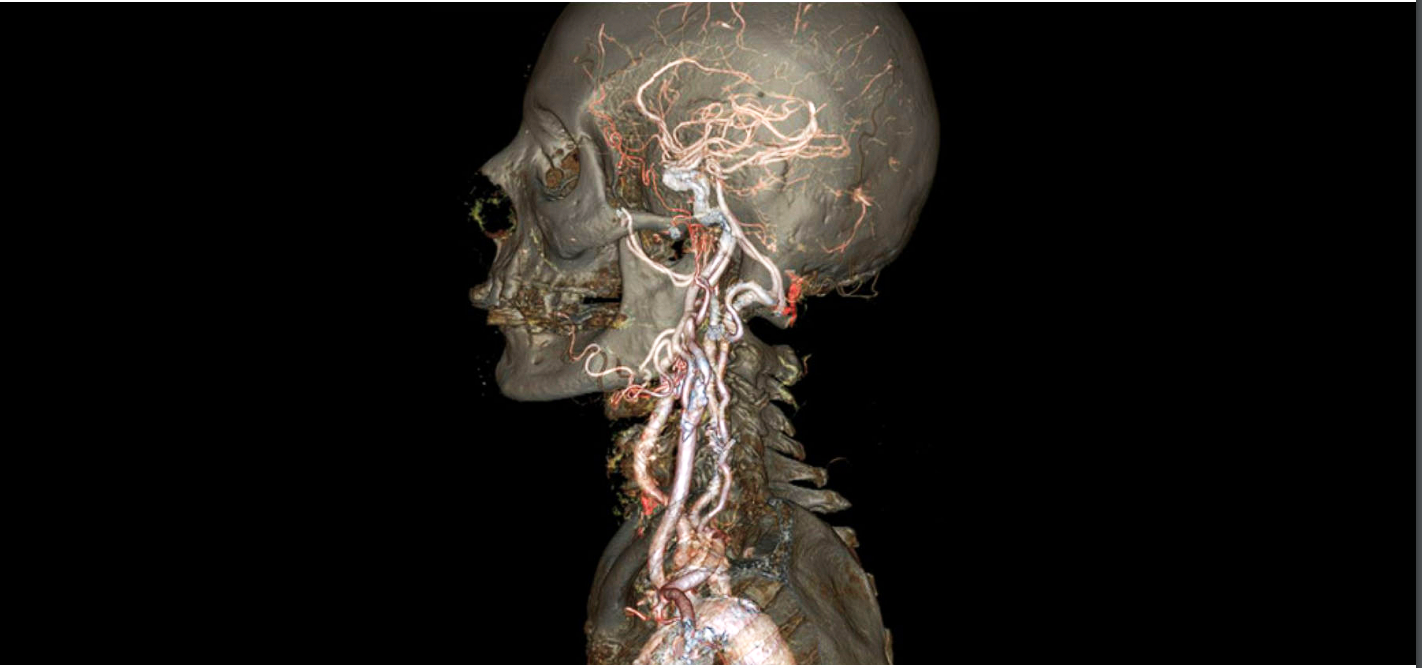
- 与texture结合:Level sets encode, e.g., constant tissue density. 将相同密度的部分连接起来形成平面结构;
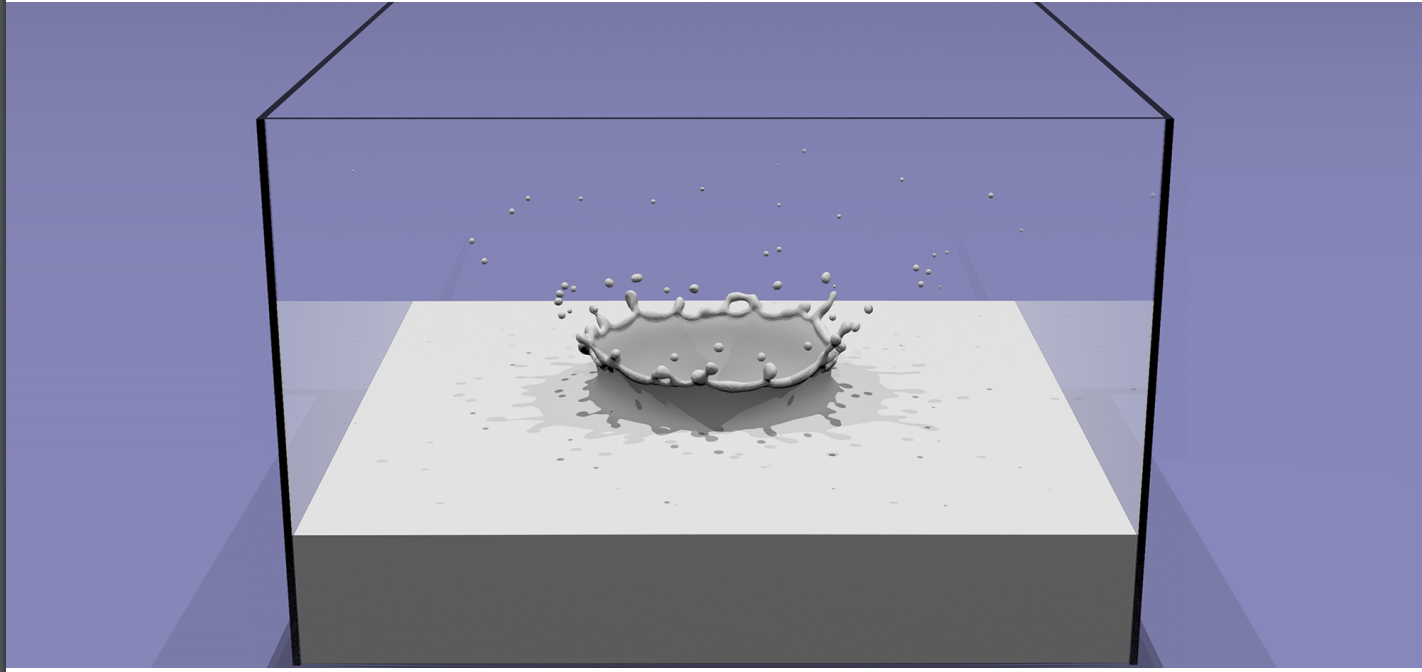
- Level set encodes distance to air-liquid boundary:将不同的水珠连接起来;
Fractals
Exhibit self-similarity, detail at all scales.
类似编程中的递归过程,是同一图形在不同scale上的展示。

问题
Hard to control shape.
因为频率很高,因此很容易造成走样。
总结
Implicit Representations的优点
- compact description (e.g., a function)
- certain queries easy (inside object, distance to surface)
- good for ray-to-surface intersection
- for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error
- easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid)
Implicit Representations的缺点
- difficult to model complex shapes

